Magnetic field measurement plays a central role in numerous areas of medicine, transportation and aerospace. The fiber optic magnetic field sensor has outstanding features such as compactness, remote sensing, low cost and high sensitivity, which has attracted great interest. However, the fiber-based magnetic field sensor is generally affected by temperature disturbances. Recently, it has been found that although temperature crosstalk can be effectively eliminated by integrating multiple sensing elements, this is done at the expense of increasing the size of the overall sensing components. Furthermore, the different spatial arrangement of multiple elements could lead to measurement errors in the discriminative detection of multiple parameters.
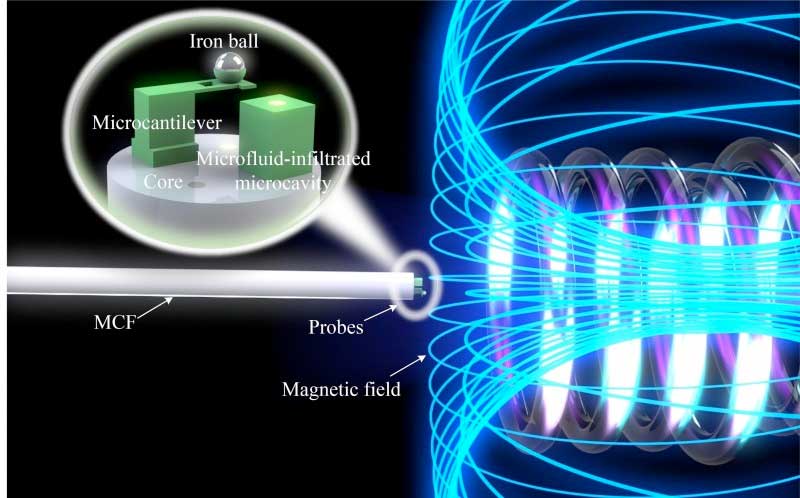
A team of researchers, led by Professor Limin Xiao from Fudan University in China, has now developed an innovative solution that addresses these challenges. In a recent study published in Light: Advanced Manufacturing, the team describes the development of ultra-compact multicore fiber (MCF) tips for the simultaneous measurement of magnetic fields and temperatures. These novel sensors were printed directly onto the tip of the fiber using two-photon polymerization (TPP), which enables a precise and miniaturized structure.
The MCF sensors consist of two different sensor elements that are placed on different cores of the fiber. A micromechanical lever containing an iron ball reacts to magnetic fields, while a microcavity filled with microfluid acts as a highly sensitive temperature element. This arrangement enables the simultaneous and discriminative detection of both parameters without temperature influences distorting the magnetic field measurement.
The 3D-printed fiber tip sensors offer a remarkable solution for applications where space for sensors is severely limited. In addition, the flexible printing technology allows the sensor designs to be adapted to specific requirements, which expands the range of applications in research and industry.
The researchers see great potential in this technology to further increase the precision and versatility of multi-core fiber sensors. The micromechanical lever could also be combined with various functional materials in order to record additional measured variables and further expand the application possibilities of the sensors.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
3DPresso is a weekly newsletter that links to the most exciting global stories from the 3D printing and additive manufacturing industry.